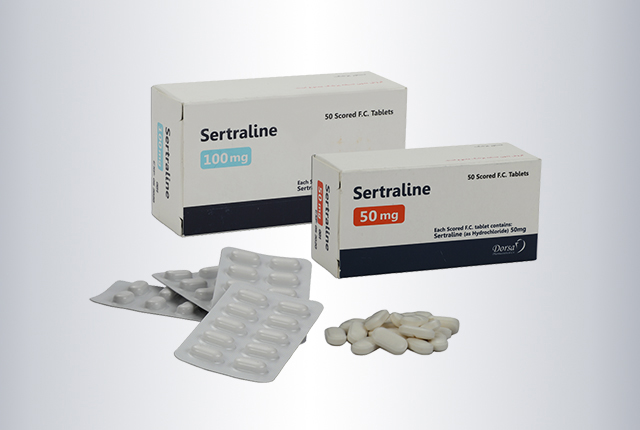
Sertraline
Here is a summary of the information about Sertraline. If there is anything you do not understand, please ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain it to you.
- Keep out of the reach of children.
- Do not use after the expiry date printed on the label.
- FDA pregnancy category: C
- Rx only.
- Do not throw away any medicines via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to throw away medicines you no longer use.
Gerenal information
Patient Information
Sertraline is one of a group of medicines called Selective Serotonin Re-uptake Inhibitors (SSRIs); these medicines are used to treat depression and/or anxiety disorders.
What Sertraline is used for:
- Depression and prevention of recurrence of depression (in adults).
- Social anxiety disorder (in adults).
- Post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) (in adults).
- Panic disorder (in adults).
- Obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) (in adults and children and adolescents aged 6-17 years old).
Tell your doctor or pharmacist before using Sertraline if :
- If you have epilepsy (fit) or a history of seizures.
- If you have suffered from manic depressive illness (bipolar disorder) or schizophrenia.
- If you have or have previously had thoughts of harming or killing yourself.
- If you have Serotonin Syndrome.
- If you have low sodium level in your blood, since this can occur as a result of treatment with
- If you are elderly as you may be more at risk of having low sodium level in your blood.
- If you have liver disease.
- If you have diabetes.
- If you have a history of bleeding disorders or have been taking medicines which thin the blood (e.g. acetylsalicyclic acid (aspirin), or warfarin) or may increase the risk of bleeding, or if you are pregnant.
- If you are a child or adolescent under 18 years old.
- If you are having electro-convulsive therapy (ECT).
- If you have eye problems, such as certain kinds of glaucoma.
- If you have been told that you have an abnormality of your heart tracing after an
- electrocardiogram (ECG) known as prolonged QT interval.
- If you have heart disease, low potassium levels or low magnesium levels, family history of QT
prolongation, low heart rate and concomitant use of medications which prolong QT interval.
Know all the medicines you take. Keep a list of them with you to show your doctor and pharmacist.
Who should not take Sertraline :
- If you are allergic to sertraline or any of the other ingredients of this medicine.
- If you are taking or have taken medicines called monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs
- such as selegiline, moclobemide) or MAOI like drugs (such as linezolid). If you stop treatment with sertraline, you must wait until at least one week before you start treatment with a MAOI.
- After stopping treatment with a MAOI, you must wait at least 2 weeks before you can start
- treatment with sertraline.
- If you are taking another medicine called pimozide (a medicine for mental disorders such as
- psychosis).
How to take your Sertraline :
- Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor or pharmacist has told you. Check with your doctor or pharmacist if you are not sure.
- Sertraline tablets may be taken with or without food.
- Take your medication once daily either in the morning or evening.
What to do if you forget to take a dose :
Do not take a double dose to make up for a forgotten dose. If you forget to take a dose, do not take the missed dose. Just take the next dose at the right time.
While taking your medicine :
- Sertraline can be taken with or without food.
- Alcohol should be avoided whilst taking Sertraline.
- Sertraline should not be taken in combination with grapefruit juice, as this may increase the level of sertraline in your body.
- If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
- Medicines like Sertraline (so called SSRIs) may cause symptoms of sexual dysfunction. In some cases, these symptoms have continued after stopping treatment.
- Psychotropic drugs such as sertraline may influence your ability to drive or use machines. You should therefore not drive or operate machinery, until you know how this medication affects your ability to perform these activities.
Call your doctor right away if you have:
- If you develop a severe skin rash that causes blistering (erythema multiforme). This may be a sign of a condition known as Stevens Johnson Syndrome, or Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN).
- Allergic reaction or allergy, which may include symptoms such as an itchy skin rash,
- breathing problems, wheezing, swollen eyelids, face or lips.
- If you experience agitation, confusion, diarrhoea, high temperature and blood pressure,
- excessive sweating and rapid heartbeat. These are symptoms of Serotonin Syndrome. In rare
- cases this syndrome may occur when you are taking certain medicines at the same time as
- Your doctor may wish to stop your treatment.
- If you develop yellow skin and eyes which may mean liver damage.
- If you experience depressive symptoms with ideas of harming or killing yourself (suicidal
- thoughts).
- If you start to get feelings of restlessness and are not able to sit or stand still after you start to
- take Sertraline. You should tell your doctor if you start to feel restless.
- If you have a fit (seizure).
- If you have a manic episode.
What to do if you take too much tablets :
If you accidentally take too much Sertraline contact your doctor at once or go to the nearest hospital casualty department. Always take the labelled medicine package with you, whether there is any medication left or not.
Symptoms of overdose may include drowsiness, nausea and vomiting, rapid heart rate, shaking,
agitation, dizziness and in rare cases unconsciousness.
Withdrawal reactions:
Side effects relating to stopping treatment (withdrawal reactions) are common, particularly if the
treatment is stopped suddenly. The risk of withdrawal symptoms depends on the length of treatment, dosage, and the rate at which the dose is reduced. Generally, such symptoms are mild to moderate. However, they can be serious in some patients. They normally occur within the first few days after stopping treatment. In general, such symptoms disappear on their own and wear off within 2 weeks. In some patients they may last longer (2-3 months or more). When stopping treatment with sertraline it is recommended to reduce the dose gradually over a period of several weeks or months, and you should always discuss the best way of stopping treatment with your doctor.
Side effects :
- Very common: insomnia, dizziness, sleepiness, headache, diarrhoea, feeling sick, dry mouth, ejaculation failure, fatigue.
- Common: chest cold, sore throat, runny nose, decreased appetite, increased appetite, anxiety, depression, agitation, decreased sexual interest, nervousness, feeling strange,
- nightmare, teeth grinding, shaking, muscular movement problems (such as moving a lot, tense muscles, difficulty walking and stiffness, spasms and involuntary movements of muscles), numbness and tingling, muscle tense, lack of attention, abnormal taste, visual disturbance, ringing in ears, palpitations, hot flush, yawning, upset stomach, constipation, abdominal pain, vomiting, gas, increased sweating, rash, back pain, joint pain, muscle pain, menstrual irregularities, erectile dysfunction, malaise, chest pain, weakness, fever, weight increased,
- Uncommon: gastroenteritis, ear infection, tumour, hypersensitivity, seasonal allergy, low thyroid hormones, suicidal thoughts, suicidal behaviour, psychotic disorder, thinking abnormal, lack of caring, hallucination, aggression, euphoric mood, paranoia, amnesia, decreased feeling, involuntary muscle contractions, passing out, moving a lot, migraine, convulsion, dizziness while standing up, abnormal coordination, speech disorder, enlarged pupils, ear pain, fast heartbeat, heart problem, bleeding problems (such as stomach bleeding), high blood pressure, flushing, blood in urine, shortness of breath, nose bleed, breathing difficulty, possible wheezing, tarry stools, tooth disorder, inflammation of the oesophagus, tongue problem, haemorrhoids, increased saliva, difficulty swallowing, burping, tongue disorder, eye swelling, hives, hair loss, itching, purple spots on skin, skin problem with blisters, dry skin, face oedema, cold sweat, osteoarthritis, muscle twitching, muscle cramps, muscular weakness, increase in frequency of urination, problem urinating unable to urinate, urinary incontinence, increase in urination, nighttime urination, sexual dysfunction, excessive vaginal bleeding, vaginal haemorrhage, female sexual
dysfunction, swelling in legs, chills, difficulty walking, thirst, increase in liver enzyme levels, weight decreased.
Reporting of side effects:
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed here.
You can also report side effects directly via the Yellow Card Scheme at: www.dorsapharma.com/ (ADR form)
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
Product specification
| Generic name | Sertraline |
| Dosage form | 50 & 100 mg white oval bi convex scored film coated tablets |
| Category | Nervous system |
| ATC code | N06AB06 |
| Package | Box of 5 Alu-PVDC blisters of 10 tablets |
| Active ingredient | Sertraline |
| Storage | Below 30°C. Protect from light & moisture. |
| Shelf life | 2 years |